
Main content:
Solar thermal power stations are positioned as peak shaving power supply and baseload power supply, which is conducive to giving full play to the comparative advantages of solar thermal power station, and the future of it is full of hope.
With the decline of the cost of solar thermal power generation, the solar thermal power station used for peak shaving power supply has technical advantages and good economy.
1. What is a solar thermal power station
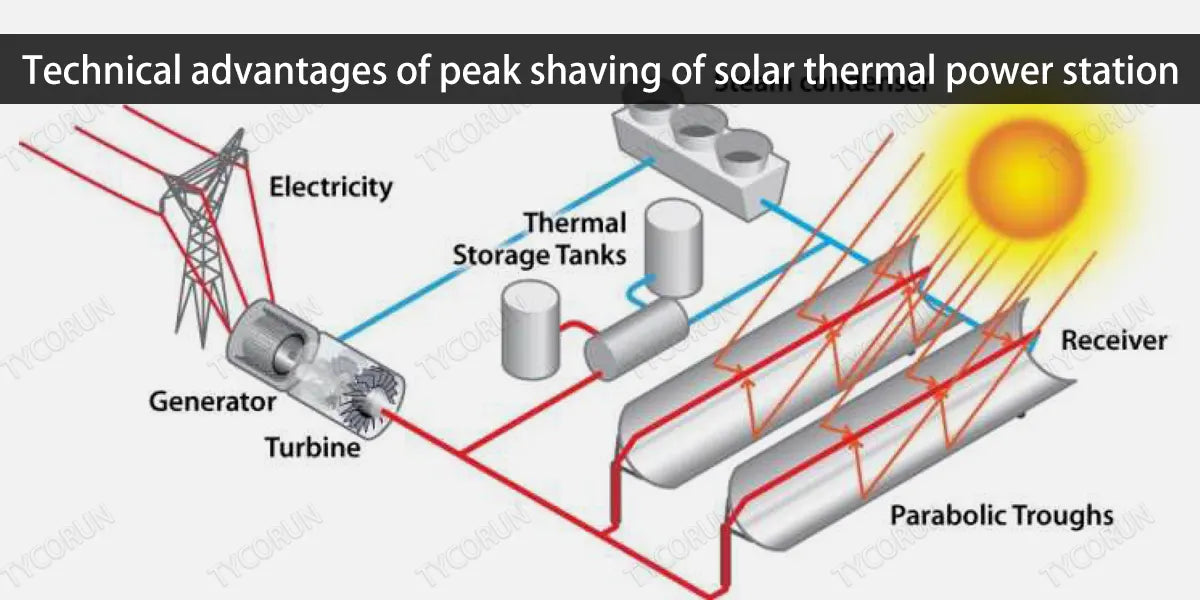
A solar thermal power station is a device that uses concentrating solar power to convert thermal energy into kinetic energy and finally into electrical energy. The second half of the power generation equipment is similar to the principle of traditional thermal power plants or nuclear power plants.
And the first half of the concentrated heat collection part is more challenging, and it is also a relatively high part of the cost.
2. Types of solar thermal power stations
Solar thermal power station can be classified according to their heat collection methods, heat storage methods, power generation methods, scale and other aspects, and the main applications in the field of power generation are:

- Trough solar thermal power station
- Tower solar thermal power station
- Dish solar thermal power station
- Linear fresnel solar thermal power station
3. Technical advantages of peak shaving of solar thermal power station
● Advantages of heat storage and energy storage technology
- Low cost: 1/10 of the cost of chemical 12v 100ah lithium ion batteries throughout the life cycle.
- High efficiency: the efficiency of heat discharge and heat storage is more than 98%.
- Long life: 0 loss or attenuation throughout the life cycle. Safe and reliable: Quickly solidifies into a stable solid state below 220°C.
● Technical advantages of CSP peak shaving
- Depth: 20% to 100% load adjustment range.
- Speed: 5–20 minute fast load change rate.
- Equipment life: The high-quality heat exchanger material ensures that the equipment can withstand the impact of rapid load changes.
4. PV power station vs solar thermal power station
|
Type |
Solar thermal power generation |
Photovoltaic power generation |
|
Scope of application |
suitable for centralized large-scale power generation |
Centralized and distributed |
|
System complexity |
Relatively complex: mirror field+ thermal system+ electrical system |
Relatively simple: photovoltaic panels+ electrical systems |
|
Energy storage systems |
Thermal energy storage, heat storage through medium (molten salt, water, etc.), long service life and low loss |
Battery energy storage system, the use of electrochemistry for energy storage has a relatively short service life and large losses |
|
Technology |
Relatively mature |
Relatively mature, and there are continuous technological breakthroughs. |
|
Advantages |
Low cost of heat storage, high efficiency, can be combined with other system |
Mature technology industry |
|
Disadvantages |
The geographical conditions are demanding |
Pollution, and the stability needs to be improved |
For many non-power industry practitioners, it may be difficult to distinguish the difference between solar thermal power generation and solar photovoltaic power generation.
The two solar power generation methods belong to completely different technical directions, and currently have their own advantages and disadvantages in terms of cost, technical characteristics, application, etc., and are briefly summarized and compared here.
5. The main risk factors faced by solar thermal power station
Judging from the main accidents in the photovoltaic power generation industry in recent years, solar thermal power stations mainly face natural disaster risks, equipment damage risks, liability risks, and light index risks during construction and operation periods.
● Natural disaster
- Strong winds and sandstorms
Most solar thermal power stations are located in the desert, and the difficulty and workload of mirror cleaning are far greater than those of conventional photovoltaic power plants.
- Torrential rain flooding
In recent years, extreme weather such as heavy rainstorms have occurred frequently in many places, and some solar thermal power stations in open and low-lying areas may face floods and strong winds.

● Equipment failure and damage
The mirror field (heliostat, tracking mechanism), collector, high-temperature working fluid conveying system, steam turbine and generator and other equipment of solar thermal power station are of high value, and equipment damage is prone to occur in harsh environments or working conditions.
- Fires in equipment and facilities
Due to the high temperature of the working fluid, the heat storage island and the sun island of the solar thermal power station and 12 volt 200ah lithium battery may cause fire due to improper operation.
- Leakage or solidification of heat transfer/storage fuid
The heat storage system configured by solar thermal power station generally uses high-temperature molten salt or heat transfer oil, which may solidify and clog when the system is not properly designed or run incorrectly, and leakage of molten salt and heat transfer oil will also bring certain safety risks.
- Damage to power generation facilities
The risks of steam turbine and generator equipment in conventional solar thermal power plants are similar to those of conventional coal-fired power stations, although the capacity is relatively small, but if there are design flaws or improper operation, they also face common risks such as equipment overspeed, blade damage, and ground short circuit.
● Personnel and management
- Lack of professional competence of O&M personnel
The operation process of solar thermal power plants requires professional personnel, and non-standard operation is likely to lead to risk accidents or improper handling of accidents, resulting in increased losses.

- Integration and installation defects
Non-standard and unsafe operation during the integration and installation of the CSP system may directly lead to equipment damage or lay potential safety hazards during operation. For example, in the process of lifting and installation, the collector pipe is prone to structural damage due to collision and extrusion.
- Lack of experience in emergency response to accidents
The number of solar thermal power stations is small, the location is remote, and it is still in the demonstration operation stage, and the operators have insufficient experience in emergency response to risks such as serious natural disasters and new equipment failures.
● Illumination index risk
- The number of hours of sunlight per year fluctuates locally
Considering improper site selection or fluctuating climatic conditions, the annual sunshine hours in some areas will fluctuate to a certain extent, and the required sunshine hours may not meet expectations, bringing the risk of profit (risk of loss of power generation).
6. Conclusion
In recent years, the development of the CSP industry has been mainly limited by construction costs, and the current investment and construction costs of solar thermal power plants are comparable to those of offshore wind power.
However, if a solar thermal power station is not equipped with heat storage, it cannot generate electricity day and night like wind power, and the cost of solar thermal power stations equipped with large-capacity heat storage remains high.
At present, the construction of a new power system with new energy as the main body is accelerating, and the various advantages and characteristics of solar energy make it have an irreplaceable position in many energy fields.The clean energy structure is also developing in the general direction of wind power, photovoltaic solar and thermal synergy, and multi-energy complementarity.
Related articles: photovoltaic power generation system, home energy storage, off grid solar batteries
















