
When consumers plan to purchase RV inverters, they are always confused between low frequency inverters and high frequency ones. What are the differences between the two? Are there any similarities? This article will compare high frequency inverter vs low frequency inverter for you.
Main content:
- What is low frequency and high frequency of inverter?
- Similarities between high frequency inverter vs low frequency inverter
- Differences between high frequency inverter and low frequency inverter
- High frequency inverter vs low frequency inverter - the characteristics
- High frequency inverter vs low frequency inverter - the performance
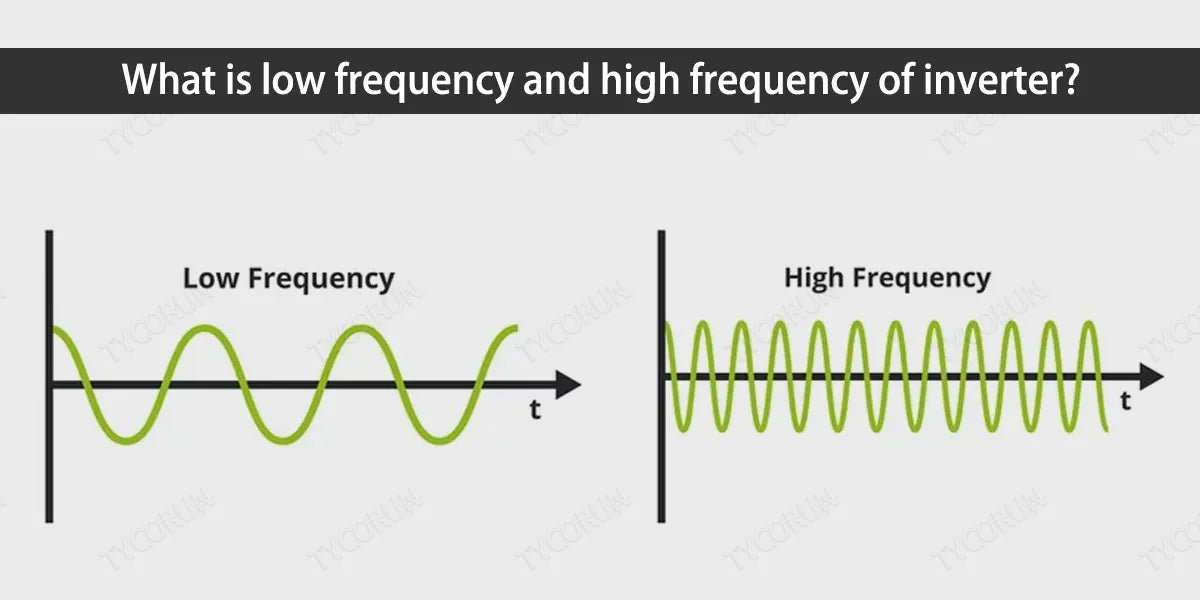
1. What is low frequency and high frequency of inverter?
The "low frequency" and "high frequency" of an inverter refer to the frequency range of the alternating current in which the inverter operates.
"Low frequency" refers to the standard alternating current frequency commonly used for public power supplies and domestic electricity like wall wart power supply. In most countries and regions, the frequency of low frequency power supply is 50Hz or 60Hz, and low frequency inverter refers to an inverter that performs inversion based on this frequency.
"High frequency" refers to a higher frequency range, usually between a few thousand Hz to tens of thousands Hz. A high frequency inverter refers to an inverter that performs inversion at this higher frequency range.
The selection for frequency range of the inverter will be influenced by the application needs and specific requirements. Low frequency inverters are usually used in larger power applications such as home power systems and industrial power, etc.
High frequency inverters are often used in applications that require smaller size, higher conversion efficiency and lower power, such as electronic equipment, solar power generation systems, electric vehicle drive systems that work with power wheels battery, etc. The appropriate frequency range of the inverter needs to be selected based on specific application needs and design requirements.
2. Similarities between high frequency inverter vs low frequency inverter
High frequency inverters and low frequency inverters are two common types of inverters. They have some differences and similarities in their working principles, application scenarios and performance characteristics. Here are the similarities:
- Function: The common goal of high frequency inverters and low frequency inverters is to convert DC power into AC power to meet specific application needs.
- Output waveform: Whether it is a high frequency inverter or a low frequency inverter, their output can be AC signals in different forms such as sine wave like TYCORUN 2000w pure sine wave inverter and power inverter 3000w, square wave or pulse wave, depending on the requirements of the application.
- Application fields: Both types of inverters are widely used in various fields, including power systems, solar power generation, UPS systems, electric drives like those work with trolling motor battery, etc. The appropriate inverter type needs to be selected based on specific application requirements, taking into account factors such as its frequency characteristics, efficiency requirements, size and weight requirements.
3. Differences between high frequency inverter and low frequency inverter
- Working frequency: Low frequency inverters usually perform inversion based on low frequency (50Hz or 60Hz), while high frequency inverters perform inversion at higher frequencies (several Hz or several + kiloHz).
- External components: High frequency inverters usually require the use of more external components to achieve high frequency switching operations, such as power transformers and capacitor filters. The low frequency inverter is simpler in design and requires a relatively small number of components.
- Size and weight: Since low frequency inverters require larger-sized components (such as large transformers), they are usually larger and heavier. In contrast, high-frequency inverters can use smaller-sized and lighter-weight components due to their use of higher frequencies, resulting in smaller overall size and weight.
- Efficiency: Since the high frequency inverter uses high-frequency switches for inversion, its switching loss is relatively small, so it has higher conversion efficiency. However, low frequency inverters will have certain switching losses during the inversion process, and their efficiency is relatively low.
4. High frequency inverter vs low frequency inverter - the characteristics
- Low frequency inverter
The low frequency inverter first inverts the DC power into low-frequency low-voltage AC power, and then boosts it through the low frequency transformer into 220V, 50Hz AC power for the load.
Features of low frequency inverter:
① When compare high frequency inverter vs low frequency inverter of the cost at low power, the cost of low frequency inverter is higher than that of high frequency inverter.
② The weight and volume of low frequency inverters are larger than those of high frequency inverters of the same power.
③ The efficiency of low frequency inverter is lower than that of high frequency inverter. The iron loss is basically unchanged when running at full load and light load. Therefore, the no-load loss of low frequency inverter is relatively large when running at light load.
④ Low frequency inverters have higher reliability than high frequency inverters and are less likely to break down.
⑤ The load capacity of low frequency inverters, especially impact load capacity, is better than that of high frequency inverters, and it can suppress high-order harmonic components in the waveform.
⑥ The structure of low frequency inverter is relatively simple, and overload and short circuit protection of low frequency inverters are easier to manufacture than high frequency ones.

- High frequency inverter
The high-frequency inverter first uses high-frequency DC/DC conversion technology to invert low-voltage direct current into high-frequency low-voltage alternating current; then, after being boosted by a high-frequency transformer, it is rectified by a high-frequency rectifier and filter circuit into a high voltage direct current above 300V, and finally through the low frequency inverter circuit, 220V low frequency alternating current is obtained for the load.
Features of high frequency inverter:
① The no-load loss of the high-frequency inverter is very small, so the inverter efficiency is high.
② The high-frequency inverter is small in size and light in weight.
③ The high-frequency inverter has a low no-load load and cannot be connected to a full-load inductive load, and its overload capacity is relatively poor.
5. High frequency inverter vs low frequency inverter - the performance
- Reliability: low frequency inverter > high frequency inverter
Low frequency inverters use silicon controlled rectifiers (SCR). Comparing high frequency inverter vs low frequency inverter, The technology of SCR has been very mature after more than half a century of development and innovation, and its ability to withstand current surges is very strong. Since the SCR is a semi-controlled device, there will be no faults such as pass-through and false triggering.
When compare high frequency inverter vs low frequency inverter, although the IGBT high-frequency rectifier used in high frequency inverters has a higher switching frequency, the IGBT has a strict voltage and current operating area when working, and its impact resistance is low. Therefore in terms of overall reliability, IGBT rectifiers are lower than SCR rectifiers.
- Environmental adaptability: high frequency inverter > low frequency inverter
The high-frequency inverter uses a microprocessor as the processing control center. Complex hardware simulation circuits are burned into the microprocessor, and the operation of the UPS is controlled by software programs. Therefore, the volume and weight are significantly reduced, the noise is also smaller, and the impact on space and environment is small, so it is more suitable for office spaces that do not have strict reliability requirements.

- Load requirements for zero-ground voltage: low frequency inverter > high frequency inverter
The neutral line of a high-power three-phase high-frequency inverter will introduce a rectifier and serve as the neutral point of the positive and negative buses. This structure will inevitably cause the high-frequency harmonics of the rectifier and inverter to couple on the neutral line, raising the neutral ground voltage, causing the zero-ground voltage at the load end to increase, which is difficult to meet the site requirements of server manufacturers such as IBM and HP for which the zero-ground voltage is less than 1V.
In addition, when switching between the mains and the generator, the high-frequency inverter often has to switch to bypass work due to the lack of neutral line, which may cause major faults such as load flashing under certain working conditions.
- Conversion efficiency: high frequency inverter > low frequency inverter
Since the high frequency inverter operates at a higher frequency, its switching period is correspondingly shorter. This reduces energy loss and current leakage during switching. At the same time, high frequency inverters usually use more advanced switching devices (such as IGBT or MOSFET, etc.), which have lower switching losses and on-resistance, thus further improving the efficiency of the inverter.
On the other hand, low frequency inverters usually require the use of larger-sized components, such as large transformers. The larger size of these components results in higher magnetic and resistive losses, which reduces the efficiency of the inverter.
If you want to want more information about Tycorun inverters, please check our power inverter 3000w pure sine wave, power inverter 2000w, 1000w pure sine wave power inverter, price of 500 watt inverter.
Related posts: 12v 100ah lithium ion batteries, Battery stores near me, RV inverter
















