
The photovoltaic inverter is the core equipment of the photovoltaic system, commonly known as the brain of photovoltaics. It is an important bridge connecting the module array and the power grid. So what are the specific characteristics and functions of photovoltaic inverters? Today we will talk about why photovoltaic inverters are so important.
Main content:
What is a photovoltaic inverter
Photovoltaic inverter is a converter that converts DC power (electricity generated by batteries and photovoltaics) into AC power (generally 220V, 50Hz sine wave), which makes it an important component of photovoltaic power generation and off grid storage batteries. Inverters are mainly used in the fields of photovoltaic, wind power, energy storage inverter and so on.
Classification of photovoltaic inverter
According to different technologies, photovoltaic inverters are mainly divided into: centralized inverters, string inverters, micro inverters, etc. At present, the market is dominated by centralized and string inverters, and micro-inverters are developing rapidly.
Centralized inverter: First aggregates the DC power generated by photovoltaics, and then converts it into AC power. The power is relatively large, generally at the MW level. Multiple parallel photovoltaic strings are connected to the DC input end of the same centralized inverter.
Generally, the high-power ones use three-phase IGBT modules, and the smaller power ones use MOS tubes. At the same time, the DSP conversion controller is used to improve the energy efficiency. The quality makes it close to a sine wave current and is mainly used in centralized photovoltaic power stations greater than 10KW.
Centralized photovoltaics mainly build large-scale photovoltaic power stations in remote areas such as deserts and mountainous areas.
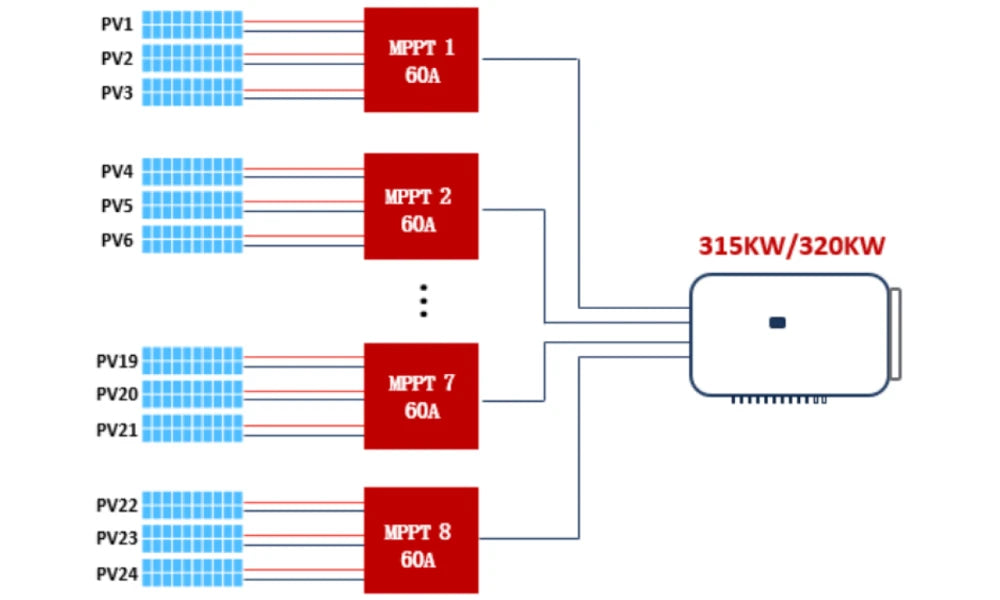
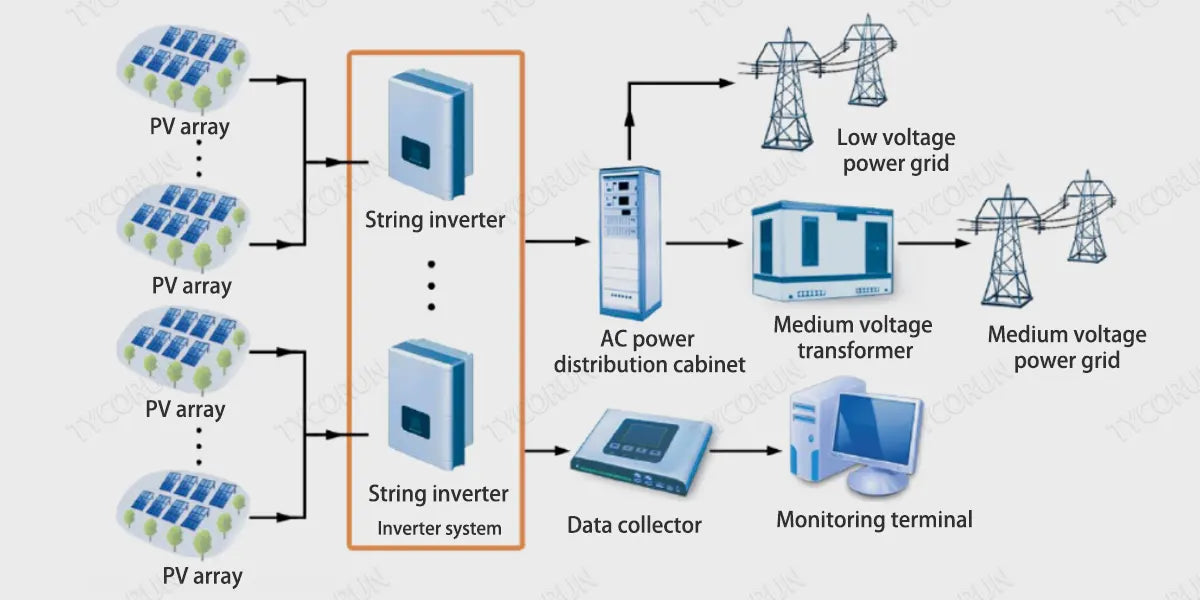
String inverter: The DC power generated by the components is directly converted into AC power and then aggregated, and the power is relatively small. The string inverter adopts a modular design, each photovoltaic array corresponds to one inverter. The DC end has a maximum power tracking function, and the AC end is connected in parallel to the grid.
Its advantage is that it is not blocked by string module differences and shadows. At the same time, it reduces the mismatch between the optimal operating point of the photovoltaic module and the inverter, thereby maximizing the power generation.
String inverter vs centralized inverter
Pros and cons Since 2020, the world's mainstream inverter manufacturers have successively released high-current string inverters. The power of string inverters used in ground power stations is mainly 320KW, and the MPPT current has been upgraded to more than 40A, supporting single string current of 20A or more.
|
Inverter type |
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
Applicable fields |
Development trends |
|
String inverter |
Small in size, light in weight, easy to transport and install; has low self-loss at night; small single unit capacity, low loss of power generation in case of failure; photovoltaic modules generate more power. |
Low conversion efficiency; high power density, high operating temperature of components , the failure rate is relatively high and the cost is relatively high. |
Distributed power stations such as household and industrial and commercial rooftops, agricultural greenhouse photovoltaics, and water surface photovoltaics, lithium RV battery, as well as centralized power stations such as hilly and large-scale ground-level power stations. |
The single-machine power is developing towards large-scale, which effectively reduces the cost of a single watt. The application of ground power stations is gradually increasing; the conversion efficiency continues to improve. |
|
Centralized inverter |
High conversion efficiency, small number of components, low cost, and high reliability. |
The single unit is large in size, heavy in weight, and difficult to transport and install. It requires separate construction and installation infrastructure; the single unit has large capacity, and the power generation loss is large in the event of failure. |
Centralized power stations such as large ground and mine. |
Continuously improve single machine capacity and reduce power station investment and power costs. |
System solutions
Centralized inverter: photovoltaic module→DC cable→DC combiner box→DC cable→centralized inverter→AC cable→step-up transformer.
String inverter: photovoltaic module→DC cable→string inverter→AC cable→AC combiner box→AC cable→step-up transformer.
Microinverter vs string inverter
Inverters in photovoltaic power generation systems with power less than or equal to 1000 watts and module-level MPPT are called micro-inverters. The function is the same as the string inverter, but because of its small size, it can be installed directly under the solar photovoltaic panel. Microinverters can convert solar energy into alternating current that people use every day.
Microinverters are divided into single-phase and three-phase. Single-phase microinverters are suitable for residential areas and small businesses. Three-phase microinverters are higher than single-phase in terms of performance, stability and efficiency, and is suitable for industry and commerce.
Each solar panel is directly connected to a microinverter in parallel. The form of micro-inverters can be set to one-to-one (each micro-inverter is connected to one photovoltaic module), one-to-two, one-to-three, one-to-four, etc., and the design can be carried out according to different microgrid models.
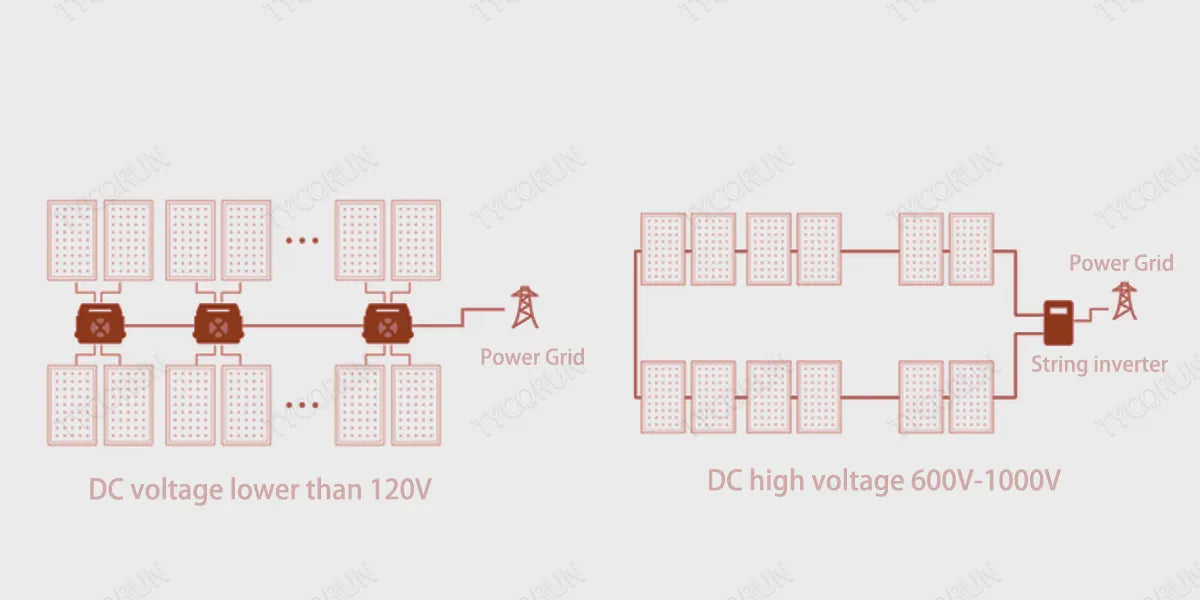
String inverters are installed in series with solar panels, so the power generated by each panel is limited, and the power generated at the top of the home solar power system will be lower. The advantage of microinverters is that they are easier to install and each solar panel can be individually monitored and optimized to achieve the highest solar efficiency.
For more information about inverters: 3000 watt car inverter, 2000 watt inverter, 1000 watt inverter, 500 watt inverter
Characteristics of photovoltaic inverter
Here are some explanation for the features and parameters of photovoltaic inverter.
Input side parameters
- Maximum input string power: The maximum DC string power allowed by the inverter.
- Rated DC power: When the power output from the component to the inverter is close to the rated DC power, the inverter can obtain the maximum AC power output.
- Maximum DC voltage: Taking the temperature coefficient into consideration, the maximum voltage of the connected string must be less than the maximum DC input voltage of the inverter.
- MPPT voltage range: A wider MPPT voltage range enables earlier power generation in the morning and more power generation after sunset.
- The number of input channels and the number of MPPT channels are not equal.
Output side parameters
- Maximum AC power: The inverter is named according to the AC output power, but some manufacturers name it according to the rated DC power.
- Maximum AC current: Directly determines the cross-sectional area of the cable and the parameter specifications of the power distribution equipment. Generally speaking, the specifications of the circuit breaker should be selected to be 1.25 times the maximum AC current.
- Rated output: There are two types of rated output: frequency output and voltage output. The primary focus is the voltage output.
- Power factor: In an AC circuit, the cosine of the phase difference (Φ) between voltage and current is called power factor, represented by the symbol cosΦ. In industrial and commercial distributed photovoltaics, reactive power compensation needs to be considered from a system perspective.
- Maximum efficiency: The maximum instantaneous conversion efficiency of the photovoltaic inverter.
The composition of photovoltaic inverter
The photovoltaic inverter is mainly composed of input filter circuit, DC/DC MPPT circuit, DC/AC inverter circuit, output filter circuit, and core control unit circuit. The electronic components include power semiconductors, integrated circuits, inductors and magnetic components, PCB circuit boards, capacitors, inductors, switching devices, connectors, etc.
And structural parts include radiators, die castings, cabinets, sheet metal parts, etc. And auxiliary materials include glue, packaging materials, plastic parts and other insulating materials.
The roles of photovoltaic inverter
Maximum power tracking function to ensure maximum output power
The current and voltage of the solar panel change with the intensity of solar radiation and the temperature of the solar cell module itself, so the output power will also change. In order to maximize the output power, it is necessary to obtain the maximum output power of the panel as much as possible. The MPPT tracking function of the inverter can solve this problem.
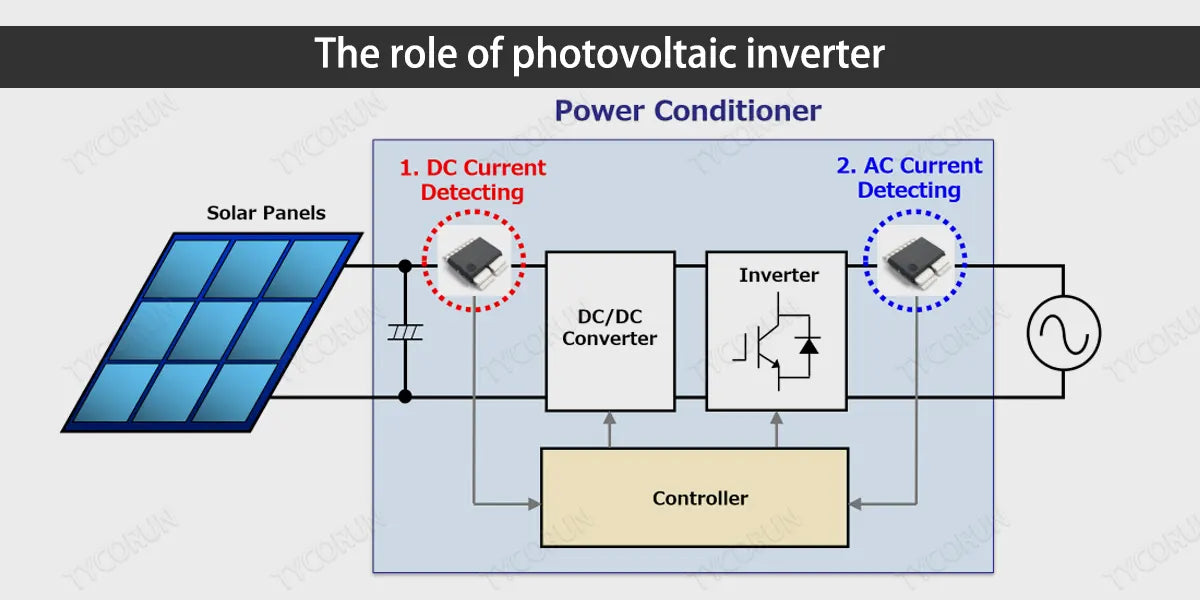
Current conversion
The inverter first tracks and analyzes the lighting conditions of solar energy, and then goes through a series of procedures such as DC boost, inverter, and filtering, and finally converts it into pure sine wave alternating current that can be accepted by the power grid. Different inverter manufacturers have big differences in quality, mainly in terms of solar energy utilization efficiency, safety and stability.
Troubleshooting
Photovoltaic power plants are generally installed in the wilderness or on rooftops. The natural environment is harsh and natural and man-made disasters will inevitably occur. Natural disasters such as typhoons, snowstorms, and sandstorms will damage the equipment. Small animals may bite the equipment, and cables may also be damaged.
The solar photovoltaic power generation system is related to the safety of people, power grids and equipment. Improper design selection and construction can also cause short circuits in the system, so solar inverters are needed to monitor system safety at all times.
The inverter has voltage, current, frequency, and insulation checking functions. When the diagnostic system fails, it will immediately alarm. If it is a safety accident that may endanger people and the power grid, stop power generation immediately and cut off the connection between the components and the power grid to prevent further expansion of the accident.
Power generation statistics
The inverter records the photovoltaic input voltage, current, power, output voltage, current, power, daily power generation, monthly power generation, and total power generation of the photovoltaic system, and the user can check it at any time.
Through the data, we can understand the quality of the components, the impact of the photovoltaic installation angle on the power generation, and compare the power generation per month in a year, which can also facilitate communication between users and manufacturers.
















