
Main content:
Lithium iron phosphate batteries and ternary lithium batteries in lithium batteries have become common choices for power batteries in new energy vehicles due to their battery high energy density, wide operating temperature range, long cycle life, and safety and reliability.
However, lithium batteries generate reversible reaction heat, Ohmic heat, polarization heat, and side reaction heat during the charging and discharging process, and their heat generation is mainly affected by battery internal resistance and charging current. Power batteries are extremely delicate, and temperature has a significant impact on their overall performance, mainly reflected in three aspects: performance, lifespan, and safety.
This article will mainly discuss lithium ion battery operating temperature from its definition, range, risks to the caveats for lithium ion battery operating temperature daily use.
The importance of lithium ion battery operating temperature
The working voltage, capacity, charge discharge rate and other parameters of lithium-ion batteries will undergo significant changes with lithium ion battery operating temperature. In addition, the performance, lifespan, and safety of lithium ion batteries are closely related to battery temperature.
Long term use at high or low temperatures can also accelerate the lifespan of lithium-ion batteries. Therefore, efforts should be made to maintain an ideal lithium ion battery operating temperature range in order to maximize the performance of lithium-ion batteries. In addition to temperature limitations, the storage temperature of lithium-ion batteries is also strictly constrained. Long term high or low temperature storage can have irreversible effects on battery performance.

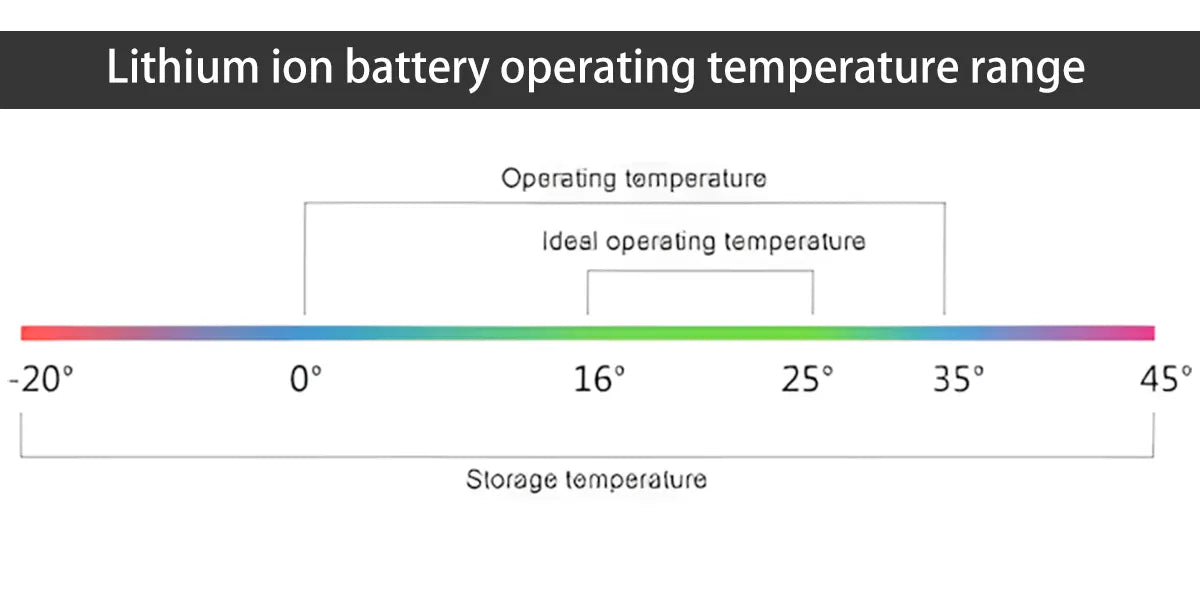
Lithium ion battery operating temperature range
It is generally believed that the optimal lithium ion battery operating temperature range for batteries is between 20 ℃ and 30 ℃. In actual projects, the optimal operating temperature for batteries needs to be determined based on the results of relevant thermal tests.
The capacity of lithium batteries will change with the increase of temperature. Through testing, it was found that the capacity increases by 0.8% for every 1 ℃ increase in temperature. However, exceeding the recommended lithium ion battery operating temperature can also damage the battery, and the cycle life and capacity of the battery will gradually decrease. According to experiments, at a room temperature of 25 ℃, if the temperature rises by 6-10 ℃, it will increase the float charging current of the battery due to high temperature, resulting in a halving of the battery's lifespan. Due to the accumulation of overcharge, the cycle life of the battery is shortened.
The capacity of lithium batteries increases with the rise of temperature. If the battery temperature rises and the total discharge remains unchanged, the depth of discharge will decrease. When the temperature of the battery rises to 45 ℃, it can extend its service life. If the battery is charged in an environment with a temperature above 50 ℃, the acid will accelerate the corrosion on the battery plates, and the increase in temperature will accelerate the aging of the battery casing.
The change in temperature causes varying degrees of attenuation in the available capacity of lithium batteries. The specific reference levels are: 70% available capacity at -10 ℃, 85% available capacity at 0 ℃, and 100% available capacity at 25 ℃. Therefore, it is normal for the performance of batteries to decline as the weather gets colder. When the temperature drops, the discharge voltage of the battery also decreases significantly. This way, the battery will reach the discharge cut-off voltage faster during low-temperature discharge, resulting in a significantly lower low-temperature battery discharge capacity than at room temperature.
What may happen to li-ion battery in low temperature
When lithium-ion batteries fall below the recommended lithium ion battery operating temperature, their available capacity decreases and their charging and discharging power is limited. If the power is not limited, it will cause the precipitation of lithium ions inside the battery, leading to irreversible capacity decay and posing safety hazards to the use of the battery. The lower the ambient temperature, the lower the activity of the active materials in the battery, the higher the internal resistance and viscosity of the electrolyte, and the more difficult it is for ions to diffuse. Moreover, at low temperatures, the diffusion rate of lithium ions in the electrode is slow, making it difficult to embed and easy to remove, resulting in a rapid decrease in capacity. Therefore, operating below the safe lithium ion battery operating temperature will significantly impact performance and lifespan.
I believe everyone has a similar feeling that lithium batteries have a shorter usage time in winter than in summer. It can be seen that the performance of lithium batteries is affected by environmental temperature. Among all environmental factors, temperature has the greatest impact on the charging and discharging performance of lithium batteries. People in the lithium battery industry generally know that the stability of the charging and discharging state of lithium batteries is greatly influenced by temperature changes. When lithium batteries are charged and discharged in high and low temperature environments, their capacity retention rate decreases.
It should be noted that the capacity of lithium-ion batteries at low temperatures does not disappear, but rather cannot be fully discharged within the normal voltage range (≥ 3.0V). If the discharge cut-off voltage can be further lowered, the remaining capacity can be discharged.
The electrochemical reactions at the electrode/electrolyte interface are related to the ambient temperature, and the electrode/electrolyte interface is considered the heart of the battery. If the temperature decreases, the reaction rate of the electrode also decreases. Assuming the battery voltage remains constant and the discharge current decreases, the power output of the battery will also decrease.
Compared to low-temperature discharge, lithium ion battery operating temperature plays an even more critical role during charging, where risks are higher. When the low-temperature charging is below 0, it will increase the internal pressure of the battery and may open the safety valve.
Firstly, low-temperature charging will quickly reach the constant voltage stage, reduce the charging capacity to a certain extent, and increase the charging time. Moreover, during low-temperature charging of lithium-ion batteries, lithium ions may not have enough time to embed into the graphite negative electrode, resulting in the formation of metal lithium dendrites on the negative electrode surface. This reaction will consume the lithium ions that can be repeatedly charged and discharged in the battery and significantly reduce the battery capacity. The precipitated metal lithium dendrites may also pierce the separator, thereby affecting safety performance.
The low-temperature discharge capacity of lithium-ion batteries may decrease, but it can be restored after room temperature charging and discharging, which is a reversible capacity loss; However, low-temperature charging can cause lithium deposition, which is a permanent capacity loss. Due to the greater harm of lithium deposition during low-temperature charging, the control of low-temperature charging for lithium-ion batteries is stricter than that of low-temperature discharge.
When charging in winter, if the outdoor temperature is low and the environment is below 0 ℃, the charging speed of the battery may decrease or even fail to charge. This is a normal phenomenon. Please place the battery in a suitable ambient temperature for charging to ensure charging effectiveness.

Caveats of lithium ion battery operating temperature in daily use
The different types of lithium batteries have different lithium ion battery operating temperature ranges. Excessive or insufficient temperature can affect the performance of lithium batteries, and in severe cases, may even shorten their lifespan.
Temperature range for lithium ion battery charging and storage
For charging and longevity, maintaining the correct lithium ion battery operating temperature is essential.
The ambient temperature range for lithium batteries should be between 20-30 ℃, and the optimal storage temperature is around 10-25 ℃. Within this temperature range, the chemical reactions inside the battery are in a relatively stable state. For example, when the temperature is 20 ℃, the ion conductivity of the electrolyte inside the lithium battery is moderate, and the activity of the electrode material can also be maintained at a good level, which is beneficial for the long-term storage of the battery.
Storing unused new lithium batteries at this temperature can minimize self discharge to the greatest extent possible. Self discharge refers to the process in which a battery gradually reduces its own charge without being connected to an external circuit. Lower temperatures can lower the chemical activity inside the battery, thereby reducing the self discharge rate. For example, in high-temperature environments, the self discharge rate of lithium batteries may significantly increase, leading to a significant decrease in battery capacity after a period of storage.
Attention should be paid to lithium-ion batteries in work
Exceeding the maximum lithium ion battery operating temperature of 100 ℃ can seriously affect lifespan and storage capacity of lithium-ion batteries, and may cause battery melting or explosion. So, please keep lithium-ion batteries away from sources of fire and other heat sources.
High temperatures ranging from 35 ℃ to 100 ℃ can also begin to affect the performance of the battery. Starting from 35 ℃ (human body temperature is generally 36.2 ℃ -37.2 ℃), the battery life is significantly affected by temperature, and the higher the temperature, the greater the impact.
Lithium ion batteries below 40 ℃ will reach the freezing point and completely freeze.
Operating below the minimum lithium ion battery operating temperature ranging from 10 ℃ to -40 ℃ can reduce battery life, but will not cause permanent damage to the battery. As long as the temperature returns to room temperature, the battery will automatically recover.

Conclusion
In general, the factors that affect batteries can be summarized as the conductivity of the electrolyte, interface impedance, SEI film, etc. These factors work together to affect the performance of the battery.
The adaptability of lithium-ion batteries to lithium ion battery operating temperature is similar to that of the human body. Both too high and too low temperatures are not conducive to their maximum function. Choosing appropriate battery materials, optimizing structural design, and customizing usage around optimal lithium ion battery operating temperature can fully unleash their performance.
Related articles: Top 10 low-temperature battery manufacturer in the world, Top 10 lithium power battery cell cans companies in the world, Top LiFePo4 power battery companies in the world
















